Introduction:
Okay, you are sitting on a LAN Network and communicating
with different hosts without any issue. But how does your computer know about
other hosts on the LAN or anyone host on the Internetwork? The mystery behind
all these operations is ARP. Address Resolution Protocol gives us a facility to
resolve IP addresses into the corresponding MAC addresses. When a computer wants to send data to some
unknown host on the network, which MAC address is not known and all the info
that computer has is just an IP address, ARP is used to resolve its L2 address.
All this data is maintained in an ARP table on each host locally, Routers and
Switches also maintain an ARP table.
Quick facts about ARP:
- ARP is defined by RFC 826
- Acronym for Address Resolution Protocol
- Used to resolve IPs to MAC address
- ARP is not a secure protocol, can be bypassed via ARP spoofing (Man in the middle attack)
- InARP or Inverse ARP is used to resolve L2 addresses into an L3 address (mostly used in ATM and FRAME Relay Networks)
- ARP stuffing is used for L2/L3 address resolution in consumer electronics devices
In order to check an ARP table that is maintained by a home
PC or computer host, just type arp –a on command prompt, the output is
something like:
Now just imagine a local LAN, on which a host wants to ping
an unknown host. In the first step it will send an ARP broadcast to all hosts
on the LAN and will enquire about the IP address. A sample capture of an ARP
broadcast capture in packet tracer is as follow, PC2 wants to communicate with
PC4:
As the MAC is not known, it’s using a broadcast address in
L2 and the packet is sent to all hosts on LAN. Now what happened on PC4?
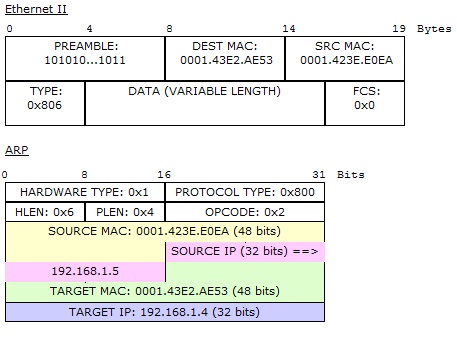
The ARP request`s target IP (192.168.1.5) got matched with
192.168.1.5, so this host will reply to PC2, so the magic that happens next is:
The address has been resolved to corresponding MAC address
as can be seen in Out Layers, so in the last stage:
As you can see in above ARP packet at the source host PC2, the
pinged L3 address of PC4 has been successfully resolved to its corresponding
MAC (Hardware) address. Packet tracer is one of the best tools to see all the
action on data packets in a real time network. To check ARP table on a router,
use show
ip arp command.
ARP due to is its open nature is susceptible to attacks. The
most common attack on ARP packets is ARP Spoofing or Man in the middle attack.
In such an attack, a hacker responds to ARP requests in disguise of the
requested L3 address. One most recent example of ARP spoofing attack was
carried out by Iran on an American drone, which was hacked and landed in Iran
by Iranian Defense forces. Same sort of experiment was carried out in a US University
in which ARP spoofing was used as an attack mechanism on Drones, and it was
quite successful. DOS (Denial of Service) attack can be carried out very easily
on the electronics devices which are using ARP stuffing, so a hacker can easily
jam all the surveillance system of some big corporation J .






No comments:
Post a Comment